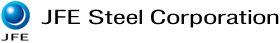News Release
JFE Steel Corporation
JFE Steel successfully demonstrates energy-saving,
reduced-emissions coke furnace
redesigned with digital twin for optimized combustion
JFE Steel Corporation announced today that a coke furnace redesigned by the company using digital-twin technology successfully achieved a five-percent energy savings and reduced its CO2 emissions by 6,600 tons, both compared to the furnace’s previous design, in the fiscal year that ended this past March. The furnace is located in the Fukuyama plant that is part of the company’s West Japan Works.
The redesigning project was supported in part with a grant from the Japanese government’s Sustainable Open Innovation Initiative.
Given that iron-making processes consume large amounts of energy and emit large amounts of CO2, JFE Steel’s pursuit of highly efficient operations in the manufacture of homogeneous, high-quality materials is expected to contribute to the company’s goal of achieving carbon neutrality in the future.
During the redesign of the Number 5, D Group coke furnace (“5D” furnace; Figure 1) in Fukuyama, a digital twin constructed in virtual space revealed that the previous furnace was hampered by insufficient air supply during the combustion process, resulting in a partial unburning of fuel. It was also determined that the basic problem was air input being controlled as an overall value. The digital twin also enabled JFE Steel to confirm that more precise control of air supply could achieve greater operational efficiency, based on which the company calculated the amount of supplemental air needed to optimize combustion. JFE Steel then applied these learnings in its redesign of the facility, which is now in commercial operation (Figure 2).
JFE Steel aims to transform all of its facilities into intelligent steel works through the use of cyber-physical systems (CPS) as part of the company’s digital transformation (DX) strategy. Digital twins are a core CPS technology in which physical systems and processes in the real world are replicated with equivalent properties in a digital model (“twin”) in a virtual space. These digital models make it possible to visualize highly inaccessible internal areas of facilities in order to optimize the design and operation of manufacturing processes for which internal conditions have conventionally been difficult to confirm via sensors or direct observation. Digital twins also make it possible to predict the effects of major changes to facilities or operations.
JFE Steel is now making extensive use of digital twins in its production processes. In 2021, for example, the company used this CPS technology to reduce the time required to restart an idle furnace from more than six months to about two months.
To overcome global competition in the steel industry, JFE Steel is pursuing revolutionary production processes through its development and application of digital twins and other CPS technologies, and implementation of DX in all facets of the company, including to the upgrading of existing businesses and the development of new businesses. JFE Steel is deeply committed to making a full and concerted effort to develop and apply new technologies that contribute to a more sustainable world.
Figure 1: Coke furnace and digital twin model
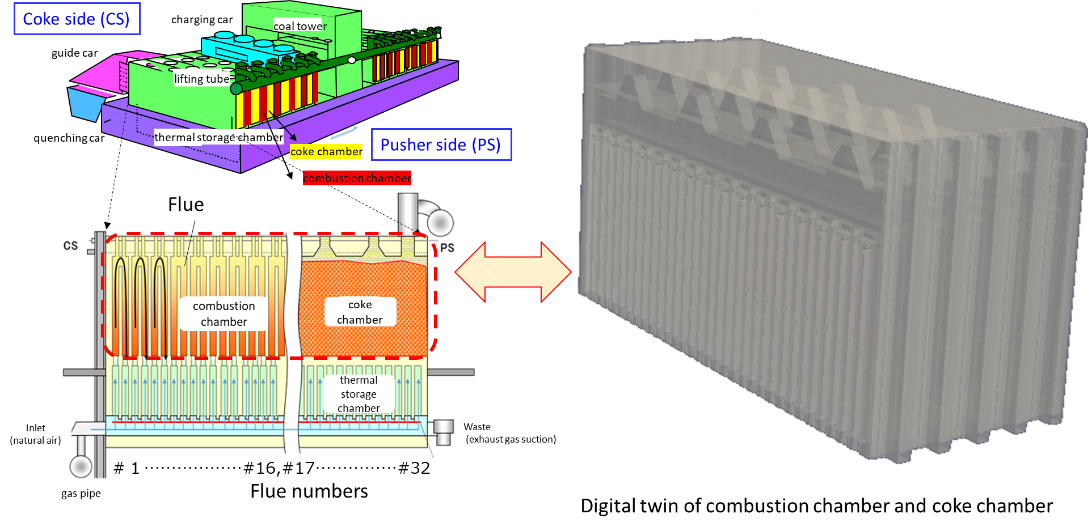
Figure 2: Optimized combustion achieved with supplemental air
About JFE Steel Corporation
JFE Steel Corporation, one of the world’s leading integrated steel producers, was established through the consolidation of NKK Corporation and Kawasaki Steel Corporation in 2003. The company operates several steelworks in Japan and numerous branch offices and affiliates throughout the world. JFE Steel leverages world-class technologies and know-how to produce a wide range of products based on its “Only One, Number One” strategy of focusing on unique and best-in-class products. The company reported consolidated sales of 2,255 billion yen and consolidated crude steel output of 23.96 million tons in the fiscal year ended March 2021.
# # #