News Release
JFE Steel Corporation
New Energy and Industrial Technology Development Organization
JFE Steel and NEDO Begin Demonstration Testing of Ferro Coke Production at medium-scale Facility
―Aiming to reduce ironmaking energy consumption and CO2 emissions by some 10% each―
The New Energy and Industrial Technology Development Organization (NEDO) and JFE Steel Corporation announced today that they completed a medium-scale ferro coke production facility with a daily production capacity of 300 tons and then began demonstration testing on October 9, aiming to develop ferro coke production technology that reduces energy consumption and CO2 emissions in the ironmaking process by approximately 10% by around 2023. The test, which is being implemented in cooperation with Kobe Steel, Ltd. and Nippon Steel Corporation, is part of a project “Technological development of Ironmaking process utilizing ferro coke”. The new facility is located at JFE Steel’s West Japan Works in Fukuyama, Japan.

Fig. 1: External appearance of medium-scale facility |

Fig. 2: Control room |

Fig. 3: Appearance of briquette on conveyor
For many years, Japan’s steel industry has been engaged in aggressive efforts to increase efficiency and reduce the carbon footprint of ironmaking. As the impact of climate change becomes more apparent, the demands for energy conservation and CO2 emissions reduction have intensified. NEDO and JFE Steel, working in cooperation with Kobe Steel and Nippon Steel, have been conducting a project “Technological development of ironmaking process utilizing ferro coke1” since fiscal 2017.
Ferro coke2 is an innovative blast furnace raw material produced from low-grade coal and low-grade iron ore in ironmaking process. The catalytic effect of metallic iron, which accounts for approximately 30% of the content of ferro coke, dramatically increases the reduction efficiency of iron ore, reducing the coke rate at the blast furnace, thereby significantly reducing the resulting amount of CO2 emissions.
The medium-scale facility is one-fifth the 1,500-ton daily production capacity envisioned for commercial operation. It comprises equipment crushing and drying, mixing and briquetting, and shaft furnace. Crushed low-grade coal, low-grade iron ore, and a binder are mixed and briquetted, and then subjected to shaft furnace to obtain ferro coke containing metallic iron.
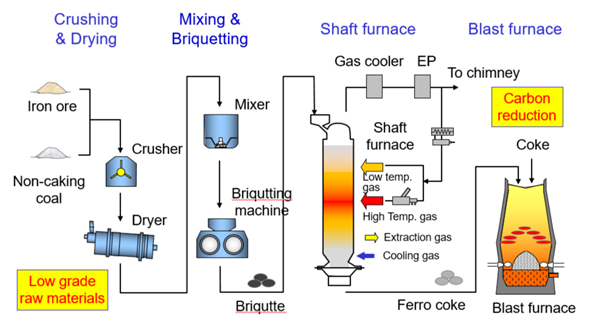
Fig. 4: Process flow of ferro coke
Future Plans
Ferro coke will be produced at the new facility until fiscal year 2022. The effects on the reducing- agent rate 3 and operational stability will be evaluated by continuously charging ferro coke into an actual blast furnace over a long period of time. The aim is to develop ferro coke production technologies to significantly reduce CO2 emissions and, conserve energy consumption in ironmaking process and enable the use of low-grade coal and iron ore, with the goal of reducing energy consumption and CO2 emissions in ironmaking process by around 10% each by around 2023.
Going forward, NEDO and the JFE Steel hope to contribute to a more sustainable world with advanced technologies that increase the efficiency and lower the carbon footprint of steelmaking.
1 The project will be carried out from fiscal 2017 to fiscal 2022 with a total planned budget of 20.1 billion yen, 50% of which will be subsidized by NEDO and the rest paid for by the participating companies. Subsidies have been granted to JFE Steel Corporation, Kobe Steel, Ltd. and Nippon Steel Corporation. The project’s joint research partners are Tohoku University and Kyushu University.
2 Ferro coke is an innovative blast furnace raw material that improves the efficiency of the iron ore reduction reaction that occurs inside a blast furnace and significantly reduces the resulting amount of CO2 emissions. Ferro coke is a composite of metallic iron and coke, which are produced by crushing, mixing and briquetting coal and iron ore, followed by heating the briquette in a shaft furnace in which continuous carbonization and iron ore reduction proceed simultaneously. Using ferro coke allows the low-grade coal and iron ore usage rates to be significantly increased compared to conventional technology. In the blast furnace, a certain amount of ordinary coke can be replaced with ferro coke. CO2 is generated by a reduction reaction of iron ore (sintered ore) by carbon monoxide (CO) inside the blast furnace. Super-fine metallic iron contained in the ferro coke becomes a catalyst in a gasification reaction (C + CO2 = 2CO) between CO2 and coke (C), which significantly improves regeneration of reducing gas (CO). As a result, CO concentration increases and the reduction reaction of iron ore (sintered ore) is possible even at low temperature, which is expected to significantly lower the reducing agent rate, resulting in energy conservation and reduced CO2 emissions.
3 The reducing agent rate (RAR) is an index of the basic consumption level of reducing materials in a blast furnace. The rate is expressed as the total weight of reducing materials (coke, pulverized coal [PC], etc.) in order to produce one ton of molten iron, regardless of the type of reducing materials. The components of reducing materials differ somewhat, and ash, which does not contribute to reduction, is also included in the weight.

Fig. 5: Photographs of ferro coke
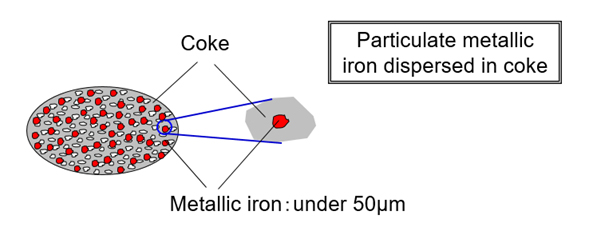
Fig. 6: Cross section of ferro coke
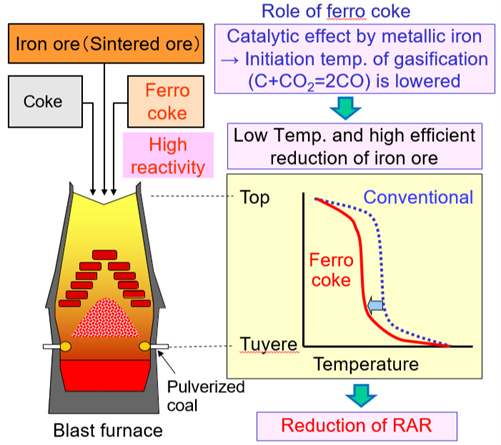
Fig. 7: Reduction mechanism of RAR by using ferro coke
Inquiries
For more information about this news release, please contact:
Messrs. Tamura or Takeda, Energy Conservation Technology Department, NEDO, Phone: 044-520-5281
JFE Steel Corporation
For general inquiries regarding other NEDO projects, please contact:
Messrs. Sakamoto or Suzuki, Public Relations Department, NEDO, Phone: 044-520-5151,
E-mail: nedo_press@ml.nedo.go.jp
About JFE Steel Corporation
JFE Steel Corporation, one of the world’s leading integrated steel producers, was established through the consolidation of NKK Corporation and Kawasaki Steel Corporation in 2003. The company operates several steelworks in Japan and numerous branch offices and affiliates throughout the world. JFE Steel leverages world-class technologies and know-how to produce a wide range of products based on its “Only One, Number One” strategy of focusing on unique and best-in-class products. The company reported consolidated sales of 3,900 billion yen in 2018 and consolidated crude steel output of 27.88 million tons in the fiscal year ended March 2019.
# # #